About
07 September 2022
Lensless camera creates 3D images from single exposure
Real-time 3D imaging method could improve robot navigation and content for 3D displays
WASHINGTON—Researchers have developed a camera that uses a thin microlens array and new image processing algorithms to capture 3D information about objects in a scene with a single exposure. The camera could be useful for a variety of applications such as industrial part inspection, gesture recognition and collecting data for 3D display systems.
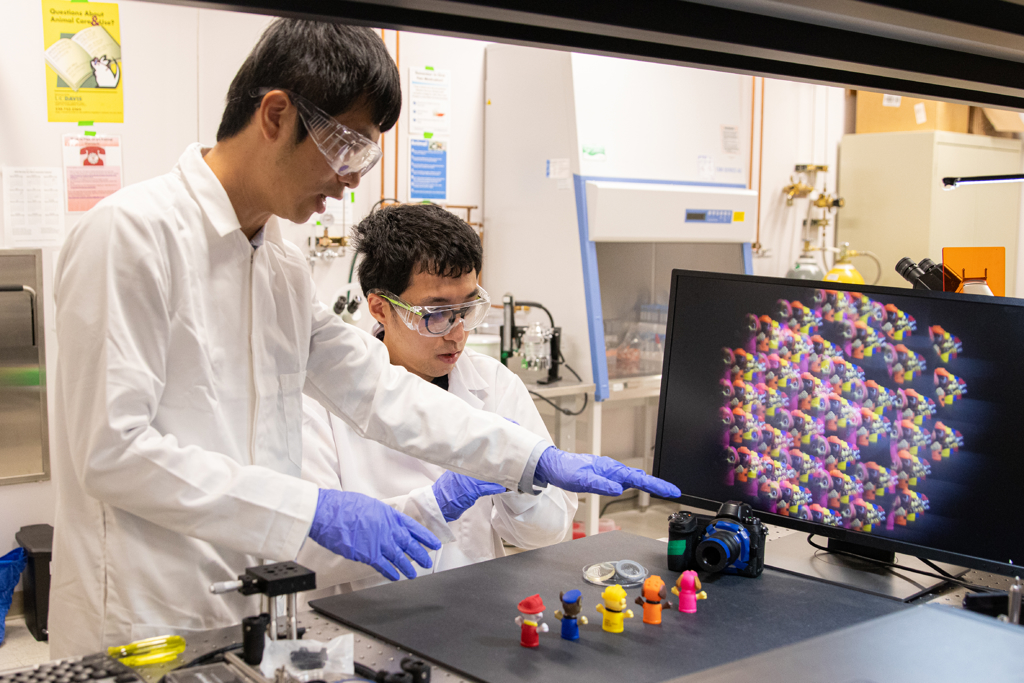

Caption: Weijian Yang and Feng Tian developed a camera that uses a thin microlens array and new image processing algorithms to capture 3D information about multiple objects in single exposure. The raw sub-images from the microarray are displayed on the monitor.
Image Credit: Savannah Luy, University of California - Davis
“We consider our camera lensless because it replaces the bulk lenses used in conventional cameras with a thin, lightweight microlens array made of flexible polymer,” said research team leader Weijian Yang from the University of California, Davis. “Because each microlens can observe objects from different viewing angles, it can accomplish complex imaging tasks such as acquiring 3D information from objects partially obscured by objects closer to the camera.”
In the Optica Publishing Group journal Optics Express, Yang and first author Feng Tian, a doctoral student in Yang’s lab, describe the new 3D camera. Because the camera learns from existing data how to digitally reconstruct a 3D scene, it can produce 3D images in real time.
“This 3D camera could be used to give robots 3D vision, which could help them navigate 3D space or enable complex tasks such as manipulation of fine objects,” said Yang. “It could also be used to acquire rich 3D information that could provide content for 3D displays used in gaming, entertainment or many other applications.”
A camera that learns
The new camera grew out of previous work in which the researchers developed a compact microscope that can image 3D microscopic structures for biomedical applications. “We built the microscope using a microlens array and thought that a similar concept could be applied for imaging macroscopic objects,” said Yang.
The individual lenses in the new camera allow it to see objects from different angles or perspectives, which provides depth information. Although other research groups have developed cameras based on single layer microlens arrays, it has been difficult to make them practical because of extensive calibration processes and slow reconstruction speeds.
“Many existing neural networks can perform designated tasks, but the underlying mechanism is difficult to explain and understand,” said Yang. “Our neural network is based on a physical model of image reconstruction. This makes the learning process much easier and results in high quality reconstructions.”
Once the learning process is complete, it can reconstruct images containing objects that are at different distances away from the camera at a very high speed. The new camera doesn’t need calibration and can be used to map the 3D locations and spatial profiles—or outlines—of objects.
Seeing through objects
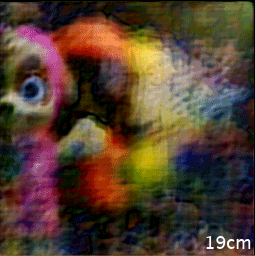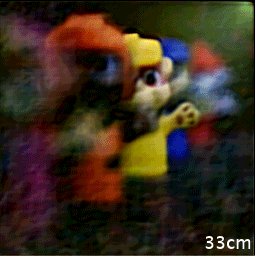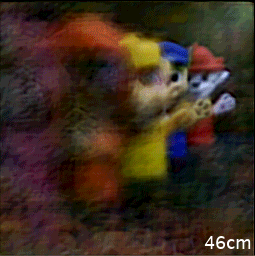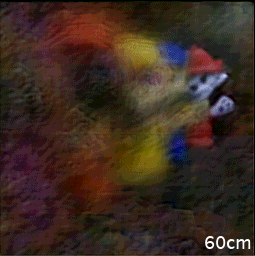
Caption: The single-shot image acquired by the new camera can be refocused and reconstructed to reveal object scenes at different distances.
Image Credit: : Feng Tian, University of California – Davis
After performing numerical simulations to verify the camera’s performance, the researchers performed 2D imaging that showed perceptually pleasing results. They then tested the camera’s ability to perform 3D imaging of objects at different depths. The resulting 3D reconstruction could be refocused to different depths or distances. The camera also created a depth map that agreed with the actual object arrangement.
“In a final demonstration we showed that our camera could image objects behind the opaque obstacles,” said Yang. “To the best of our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of imaging objects behind opaque obstacles using a lensless camera.”
The researchers are currently working to reduce artifacts, or errors, that appear in the 3D reconstructions and to improve the algorithms to gain even higher quality and speed. They also want to miniaturize the overall device footprint so it could fit into a cellphone, which would make it more portable and enable more applications.
“Our lensless 3D camera uses computational imaging, an emerging approach that jointly optimizes imaging hardware and object reconstruction algorithms to achieve desired imaging tasks and quality,” said Yang. “With the recent development of low-cost, advanced micro-optics manufacturing techniques as well as advancements in machine learning and computational resources, computational imaging will enable many new imaging systems with advanced functionality.”
Paper: F. Tian, W. Yang, “Learned lensless 3D camera,” Opt. Express, 30, 19, 34479-34496 (2022).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.465933
About Optica Publishing Group
Optica Publishing Group is a division of the society, Optica, Advancing Optics and Photonics Worldwide. It publishes the largest collection of peer-reviewed and most-cited content in optics and photonics, including 18 prestigious journals, the society’s flagship member magazine, and papers and videos from more than 835 conferences. With over 400,000 journal articles, conference papers and videos to search, discover and access, our publications portfolio represents the full range of research in the field from around the globe.
About Optics Express
Optics Express reports on scientific and technology innovations in all aspects of optics and photonics. The bi-weekly journal provides rapid publication of original, peer-reviewed papers. It is published by Optica Publishing Group and led by Editor-in-Chief James Leger of the University of Minnesota, USA. Optics Express is an open-access journal and is available at no cost to readers online. For more information, visit Optics Express.
Media Contact
